بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
السلامه عليكم ورحمة الله وبركاته . البروتوكول اولا , يمثل TCP/IP من الناحية العلمية مجموعة من الوسائل التي تمكن الحواسيب المشبكة من الاتصال فيما بينها ، بصرف النظر عما اذا كانت تنتمي الي الشبكة ذاتها او إلي شبكات منفصلة ، وما اذا كانت من نوع واحد او من انواع مختلفة ، ويمثل TCP/IP مجموعة من المعايير القياسية، المستقلة عن منصات العتاد التي يؤمن الاتصال فيما بينها، وهو يجسر الفجوة بين الحواسيب ونظم التشغيل والشبكات المختلفة، و TCP/IP كذلك البروتوكول الذي يحرك شبكة الانترنت العالمة التي يعود اليهاا الفضل الأساسي في شهرته الواسعة ... تقوم بروتوكولات TCP/IP علي تقنية Packet Switching تبديل الرزم ... وتبديل الرزم تعني تقسيم البيانات الي رزم Packet منفصلة وحيدة الهوية التي تشكل بعد جمعها البيانات كليا ..
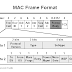
ارتباط رأس البيانات
تعويض 0-5: عنوان الوجهة
بايت الستة الأولى من إطار إيثرنت تشكل عنوان الوجهة. يحدد عنوان الوجهة التي محول يتم إرسال بيانات الإطار. العنوان الوجهة من كل منها يحدد رسالة البث التي يتم قراءتها في جميع محولات إيثرنت المستقبلة.
يتم تعيين البايتات الثلاثة الأولى من عنوان الوجهة من قبل IEEE إلى البائع من محول، وتعتبر خاصة إلى البائع.
شكل عنوان الوجهة غير متطابقة في جميع تطبيقات إيثرنت.
تعويض 11/6: عنوان المصدر
بايت الستة المقبلة من إطار إيثرنت تشكل عنوان المصدر. يحدد عنوان المصدر من محول الذي نشأت الرسالة. مثل عنوان الوجهة، البايتات الثلاثة الأولى تحدد بائع البطاقة.
شكل عنوان المصدر مطابق في جميع تطبيقات إيثرنت.
تعويض 12-13: الطول
بايت 13 و 14 من إطار إيثرنت تحتوي على طول البيانات في الإطار، وليس بما في ذلك الديباجة، 32 بت CRC، العناوين DLC، أو الحقل طول نفسه. إطار إيثرنت لا يمكن أن يكون أقصر من 64 بايت، وأنه لم يعد من 1518 بايت في الطول الإجمالي.
من 802.2 المنطقي لينك تحكم رأس (LLC)
بعد ارتباط رأس بيانات غير المنطقي ربط تحكم رأس، الذي يوصف في IEEE 802.2 مواصفات. الغرض من رأس LLC هو توفير "ثقب في السقف" طبقة وصلة البيانات. لتحديد إلى أي ذاكرة العازلة محول يضع الإطار البيانات، رأس LLC يسمح للطبقات العليا لمعرفة مكان العثور على البيانات.
تعويض 14: DSAP
وDSAP، أو الوجهة نقطة وصول خدمة، هو حقل 1 بايت تعمل فقط كمؤشر إلى مخزن ذاكرة مؤقت في محطة الاستقبال. وهو يروي NIC تلقي فيه العازلة لوضع هذه المعلومات. هذه الوظيفة هي الحاسمة في الحالات التي يكون فيها المستخدمون يعملون مداخن بروتوكول متعددة، الخ ...
من أجل تحديد أن هذا هو الإطار SNAP، يتم تعيين DSAP إلى AA عرافة.
تعويض (15): SSAP
وSSAP، أو خدمة المصدر نقطة وصول هو مماثل لDSAP، ويحدد نقطة وصول خدمة (SAP) من عملية الإرسال.
من أجل تحديد أن هذا هو الإطار SNAP، يتم تعيين SSAP إلى AA عرافة.
تعويض 16: بايت تحكم
عقب برامج التكيف الهيكلي هو مجال التحكم بايت واحد يحدد نوع LLC إطار أن هذا هو.
للشبكة الفرعية الوصول البروتوكول (SNAP) رأس
تنسيق الإطار PPP عامة
(صفحة 1 من 4)
كل الرسائل المرسلة باستخدام PPP يمكن اعتبار أي بيانات أو معلومات التحكم. كلمة "بيانات" يصف مخططات طبقة أعلى نحاول نقل هنا في طبقة اثنين؛ هذا ما لدينا "العملاء" تعطي لنا أن نرسل. يتم استخدام المعلومات السيطرة على إدارة هذه العملية من البروتوكولات المختلفة داخل PPP نفسها. على الرغم من بروتوكولات مختلفة في جناح PPP استخدام العديد من أنواع الإطارات، وعلى أعلى المستويات جميعها تندرج في واحد، وشكل الإطار العام.
في نظرة عامة على PPP ذكرت أن العملية الأساسية للجناح يستند على بروتوكول ISO الرفيع المستوى بيانات ارتباط التحكم (HDLC). هذا يصبح واضحا جدا عندما ننظر إلى هيكل PPP إطارات عموما، أنها تستخدم نفس الشكل الأساسي كما HDLC، وحتى إلى نقطة بما في ذلك بعض المجالات التي ليست ضرورية تماما لPPP نفسها. التغيير الرئيسي الوحيد هو إضافة حقل جديد لتحديد بروتوكول البيانات مغلفة. يتم تعريف الهيكل العام للإطارات PPP في RFC 1662، و "رفيق" لPPP معيار RFC الرئيسي 1661.
إيثرنت، IEEE 802.3 يحدد صيغ الإطار أو إطار الهياكل التي يتم تطويرها داخل طبقة MAC من مكدس البروتوكول.
أساسا يستخدم نفس هيكل الإطار لأنواع مختلفة من إيثرنت، وإن كانت هناك بعض التغييرات على هيكل الإطار تمديد ينبغي أن تكون هناك حاجة إلى أداء النظام هذا. مع سرعات عالية ومتنوعة من الوسائط المستخدمة، وهذا الشكل الأساسي يحتاج في بعض الأحيان إلى تكييفها لتلبية الاحتياجات الفردية للنظام النقل، ولكن هذا لا يزال تحديد داخل تعديل / تحديث لأنه نظرا إيثرنت البديل.
10/100 ميغابايت في الثانية إيثرنت MAC تنسيق الإطار البيانات
ونظرا لMAC تنسيق الإطار البيانات الأساسية للإيثرنت، IEEE 802.3 المستخدمة في أنظمة 10 و 100 ميغابت في الثانية أدناه:
إيثرنت الإطار
الأساسي تنسيق الإطار إيثرنت MAC البيانات
يتكون الإطار الأساسي لسبعة عناصر انقسام بين ثلاثة مجالات رئيسية هي: -
رأس
الديباجة (PRE) - وهذا هو سبعة بايت ويتكون من نمط بالتناوب الآحاد والأصفار، وهذا يبلغ محطات الاستقبال أن الإطار بدأ فضلا عن تمكين المزامنة. (10 ميغابايت في الثانية إيثرنت)
بداية محدد الإطار (قوات العمليات الخاصة) - وهذا يتكون من بايت واحد ويحتوي على نمط بالتناوب من الآحاد والأصفار ولكن تنتهي في اثنين منها.
عنوان الوجهة (DA) - يحتوي هذا الحقل على عنوان المحطة التي يقصد البيانات. أكثر قليلا اليسار يشير إلى ما إذا كانت الوجهة عنوان الفردي أو عنوان المجموعة. يرمز عنوان على حدة بواسطة صفر، في حين أن واحد يشير إلى عنوان المجموعة. بت المقبل في DA إلى ما إذا كان عنوان يدار على الصعيد العالمي، أو المحلي. إذا كانت تدار عنوان عالميا بت هو صفر، واحد منه تدار محليا. ثم هناك 46 بت المتبقية. وتستخدم هذه لعنوان الوجهة نفسها.
عنوان المصدر (SA) - عنوان المصدر ويتكون من ستة بايت، ويتم استخدامه لتحديد محطة الإرسال. كما هو دائما عنوان الفردي أكثر قليلا اليسار هو دائما صفر.
طول / نوع - هذا الحقل اثنين بايت في طول. أنه يوفر المعلومات MAC ويشير إلى عدد من أنواع البيانات العميل التي تم تضمينها في حقل البيانات من الإطار. ويمكن أيضا أن تشير إلى نوع ID الإطار إذا الإطار يتم تجميعها باستخدام شكل اختياري. (IEEE 802.3 فقط).
الحمولة
بيانات - هذه الكتلة تحتوي على بيانات الحمولة وأنه قد يكون ما يصل إلى 1500 بايت. إذا كان طول الحقل أقل من 46 بايت، يضاف ثم الحشو بيانات لجلب طوله يصل إلى الحد الأدنى المطلوب من 46 بايت.
مقطورة
راجع الإطار تسلسل (FCS) - هذا الحقل هو أربعة بايت. أنه يحتوي على 32 بت معطل دوري تحقق (CRC) التي يتم إنشاؤها على مدى DA، SA، طول / نوع وحقول البيانات.
1000 ميغابت في الثانية إيثرنت MAC تنسيق الإطار البيانات
يتم تعديل MAC تنسيق الإطار البيانات الأساسية للإيثرنت قليلا ل1GE، نظم 802.3z IEEE. عند استخدام 1000BASE-X معيار، هناك حد أدنى لحجم الإطار من 416bytes، و1000BASE-T هناك حد أدنى لحجم الإطار من 520bytes. لاستيعاب هذا، يضاف امتدادا حسب الاقتضاء. هذا هو حقل تمديد متغير غير البيانات إلى أي الإطارات التي هي أقصر من الحد الأدنى المطلوب طول.
1GE / 1000 ميغابت في الثانية إيثرنت الإطار
1GE / 1000 تنسيق الإطار ميغابت في الثانية إيثرنت MAC البيانات
نقل نصف مزدوج
يتضمن هذا الأسلوب الوصول استخدام CSMA / CD وتم تطويره لتمكين عدة محطات لتبادل متوسطة نقل نفسه من دون الحاجة إلى التبديل، وأجهزة التحكم في الشبكة أو فتحات الوقت المخصص. كل محطة قادرة على تحديد متى أنها قادرة على إرسال وهذه الشبكة هو التنظيم الذاتي.
بروتوكول CSMA / CD يستخدم لإيثرنت ومجموعة متنوعة من التطبيقات الأخرى تقع في ثلاث فئات. الأول هو تحسس الناقل. هنا كل محطة تنصت على شبكة لحركة المرور ويمكن الكشف عن عندما الشبكة هادئة. والثاني هو الجانب المتعدد الوصول حيث تكون قادرة على تحديد لأنفسهم ما إذا كان ينبغي إحالة المحطات. العنصر الأخير هو اصطدام الكشف عن عنصر. على الرغم من المحطات قد تجد الشبكة مجانا، فإنه لا يزال من الممكن أن محطتين سوف تبدأ في نقل تقريبا في نفس الوقت. وإذا حدث ذلك فإن مجموعتين من البيانات التي يتم إرسالها سوف تتصادم. إذا حدث ذلك فإن المحطات يمكن الكشف عن هذا، وأنها سوف توقف الإرسال. وبعد ذلك تتراجع كمية عشوائية من الوقت قبل محاولة إعادة الإرسال. التأخير عشوائي مهم لأنه يمنع المحطتين بدءا لنقل معا مرة ثانية.
ملاحظة: وفقا للمادة 3.3 من المعيار IEEE 802.3، كل ثمانية من الإطار إيثرنت، مع استثناء من FCS، ينتقل الترتيب المنخفض قليلا أولا.
الازدواج الكامل
خيار آخر يسمح به إيثرنت MAC هو الازدواج الكامل مع الإرسال في كلا الاتجاهين. هذا هو المسموح به فقط على من نقطة إلى نقطة وصلات، وأنه هو أبسط من ذلك بكثير لتنفيذ من استخدام النهج / CD CSMA فضلا عن توفير أعلى بكثير معدلات الإنتاجية نقل عند استخدام الشبكة. لا هو فقط هناك حاجة لتحديد موعد الإرسال عندما لم نقل أخرى جارية، كما أن هناك اثنين فقط من محطات في الارتباط، ولكن باستخدام وصلة الازدواج الكامل، والإرسال معدل كامل ويمكن إجراء في كلا الاتجاهين، وبالتالي مضاعفة عرض النطاق الترددي فعالة.
عناوين إيثرنت
وتعطى كل شبكة إيثرنت بطاقة واجهة (NIC) معرف فريد يسمى عنوان MAC. يتم تعيين هذا من قبل الشركة المصنعة للبطاقة وكل منتج يتوافق مع معايير IEEE يمكن أن تنطبق على السلطة التسجيل IEEE لمجموعة من الأرقام لاستخدامها في منتجاتها.
عنوان MAC يتكون من عدد 48 بت. ضمن عدد البتات 24 الأولى تحدد الشركة المصنعة وكما هو معروف معرف منتج أو التنظيمي فريد معرف (OUI) وهذا تم تعيينه من قبل سلطة التسجيل. يتم تعيين النصف الثاني من عنوان من قبل الشركة المصنعة وكما هو معروف تمديد ID متنها.
وعادة ما يتم برمجتها عنوان MAC في الأجهزة بحيث لا يمكن تغييره. لأن يتم تعيين عنوان MAC لNIC، وهو يتحرك مع الكمبيوتر. حتى إذا تحرك بطاقة واجهة إلى موقع آخر في جميع أنحاء العالم، ويمكن الوصول للمستخدم ليتم إرسال الرسالة إلى عنوان MAC معين.
Peace, mercy and blessings of God. Protocol First, a TCP / IP from a scientific point of a set of tools that enable computers networked to communicate with each other, regardless of whether they belong to the same network or to the separate networks, and whether of one type or of different types, and a TCP / IP set of standards, independent of hardware platforms that believes in contact with each other, which bridges the gap between computers and various operating systems and networks, and TCP / IP as well as the protocol that drives the Internet, which the scientist back Allehaa main merit of his fame in the vast ... The Protocols TCP / IP on technology Packet Switching switch packets ... and packet switch means split the data into packets Packet separate single identity that was formed after the data collected entirely ..
The head of the data link
Compensation 0-5: destination address
The first six bytes of the Ethernet frame form the destination address. Determines the destination adapter frame data is sent address. The destination of each title identifies the broadcast message that is read in all receiving Ethernet adapters.
The appointment of the first three bytes of the destination address by the IEEE to the seller of the adapter, and are specific to the seller.
The destination address of the form is identical in all Ethernet applications.
11/6 compensation: source address
The next six bytes of Ethernet frame form the source address. It determines the source address of the adapter, which originated the message. Such as destination address, the first three bytes define the card vendor.
Source (s) with the title of the form in all Ethernet applications.
Compensation 12-13: Length
13 and 14 bytes of Ethernet frame contains the length of the data in the frame, not including the preamble, 32-bit CRC, titles DLC, or the same length of the field. Ethernet frame can not be shorter than 64 bytes, and no longer than 1518 bytes in total length.
From 802.2 Logical Link Control head (LLC)
After illogical data link top link control head, which is described in the IEEE 802.2 specification. The purpose of the LLC header is to provide a "hole in the ceiling" data link layer. To determine any buffer memory adapter puts frame data, LLC header allows the upper layers to know where to find the data.
Compensation 14: DSAP
And DSAP, or destination service access point, is a field 1 byte operate only as a pointer to a temporary memory store in the receiving station. It tells NIC receive buffer in which to put this information. This function is critical in cases where users are running multiple protocol stacks, etc ...
In order to determine that this is the SNAP frame, DSAP is set to AA hex.
Compensation (15): SSAP
And SSAP, or access point source service is similar to DSAP, and identifies service access point (SAP) of the transmission process.
In order to determine that this is the SNAP frame, the SSAP set to AA hex.
Compensation 16: Byte Control
Following the structural adjustment programs is a field of one byte Control determines the type of LLC frame that is.
Sub-Network Access Protocol (SNAP) header
General PPP frame format
(Page 1 of 4)
All messages sent using PPP can be any data or control information considered. The word "data" describes the top layer schemes are trying to transfer here in two layer; this is what our "customers" give us to send. The information is used to control the management of this process of the various protocols within the PPP itself. Despite the different protocols in a suite PPP use many types of tires, and at the highest levels, all of which fall into one, and the form of the general framework.
In an overview of the PPP said that the primary operation of the wing is based on the ISO Data Link Control Protocol High-level (HDLC). This becomes very clear when we look at the overall structure of the PPP frames, they use the same basic shape as HDLC, and even to the point of including some areas that are not strictly necessary for the PPP itself. The only major change is the addition of a new field to determine the encapsulated protocol data. It is defined as the overall structure of PPP frames in RFC 1662, and "companion" for the main PPP RFC 1661 standard.
Ethernet, IEEE 802.3 defines the frame formats or frame structures that are developed within the MAC layer of the protocol stack.
Basically uses the same frame structure for various types of Ethernet, though there have been some changes to the frame structure extension should be no need for this system performance. With high speed and variety of media used, and this basic shape sometimes it needs to be adapted to meet the individual needs of the transportation system, but this is still determining inside Edit / update that due Ethernet alternative.
10/100 Mbps Ethernet MAC frame format data
Given the MAC frame format of basic data for Ethernet, IEEE 802.3 used in the 10 and 100 megabits per second systems below:
Ethernet frame
Basic Ethernet MAC frame format data
The basic framework consists of seven members split between three main areas: -
Head
Preamble (PRE) - This is a seven-byte it consists of a pattern of alternating ones and zeros, and this has a receiving stations that began framework as well as syncing enabled. (10 Mbps Ethernet)
Set the beginning of the frame (SOF) - This consists of a single byte contains alternating pattern of ones and zeros, but in the end the two of them.
The destination address (DA) - This field contains the data station which is intended address. A little more left indicates whether the destination is an individual or group address. It symbolizes the address on the unit by zero, while the one refers to the group title. The next bit in the DA to whether the title is managed on a global level, or local. If managed globally-bit address is zero, and one of it is managed locally. Then there's the remaining 46 bits. These are used to address the same destination.
The source address (SA) - the source address and consists of six bytes, and is used to determine the transmission station. As it is always the individual title a little more left is always zero.
Length / Type - This field is two bytes in length. It provides information and MAC refers to the number of customer data that are included in the data field of the frame types. It also can indicate the type of ID window if the frame is assembled using the optional form. (IEEE 802.3 only).
Load
Data - This block contains the payload data and it may be up to 1500 bytes. If the field length of less than 46 bytes, then padding is added to bring data up to the desired length of 46 bytes minimum.
Trailer
See the frame sequence (FCS) - This field is four bytes. It contains a 32-bit Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) that are created over the DA, SA, Length / type and data fields.
1000 Mbps Ethernet MAC frame format data
MAC is adjusted coordinate basic data of the Ethernet frame for a little 1 GE, IEEE 802.3z systems. When using 1000BASE-X standard, there is a minimum frame size of 416bytes, and 1000 BASE-T there a minimum frame size of 520bytes. To accommodate this, add an extension as appropriate. This is an extension of the non-variable data to any frames that are shorter than the minimum required length of the field.
1GE / 1000 Mbps Ethernet frame
1GE / 1000 frame format Mbps Ethernet MAC data
Half-duplex transmission
This method involves the use of access CSMA / CD was developed to enable multiple stations to share the same transmission medium without the need to switch, and control devices in the network or the allotted time slots. Each station is able to determine when it is able to send and the network is self-regulation.
Protocol CSMA / CD is used for Ethernet and a variety of other applications fall into three categories. The first is the Carrier Sense. Here each station eavesdrop on network traffic and can detect when a quiet network. The second is a multi-access side where they are able to determine for themselves whether they should refer the stations. The last item is the collision detection element. Although the stations may find the network for free, it is still possible that the two will begin to transfer almost at the same time. If that happens, the two sets of data that are sent will collide. If that happens, the stations can detect this, and they will stop transmission. And then back down a random amount of time before attempting retransmission. Random delay is important because it prevents the two stations starting to move together again.
Note: In accordance with Article 3.3 of the IEEE 802.3 standard, all eight of the Ethernet frame, with the exception of the FCS, the low-order bit is transmitted first.
Full duplex
Another option allowed by the Ethernet MAC is full duplex with the transmission in both directions. This is allowed only on the point-to-point links, and it is much simpler to implement than the use of approaches / CD CSMA as well as providing a much higher productivity transfer rates when using the network. Neither he only needed to determine the dispatch date when no other transfer under way, as there are only two stations in the link, but using the link full duplex, and transmission full rate can be made in both directions, thus doubling the width effective bandwidth.
Ethernet addresses
And given all Ethernet network interface card (NIC) a unique identifier called a MAC address. This is set by the manufacturer of the card and every product complies with the IEEE standards can be applied to the IEEE Registration Authority set of numbers to be used in their products.
MAC address consists of a 48-bit number. The number of bits within the first 24 identifies the manufacturer and is also well-known product ID or organizational unique identifier (OUI) and this is assigned by the registration authority. It is assigned the second half of the title by the manufacturer and is known to extend the ID board.
It is usually programmed MAC address in the hardware so that it can not be changed. The MAC's because the NIC address is assigned, it moves with your computer. Even if the move card interface to another location all over the world, and can be accessed for the user to the message is sent to a specific MAC address.